EV Technology Today - Chargers
- Arun Bhatia

- Jun 20, 2022
- 4 min read
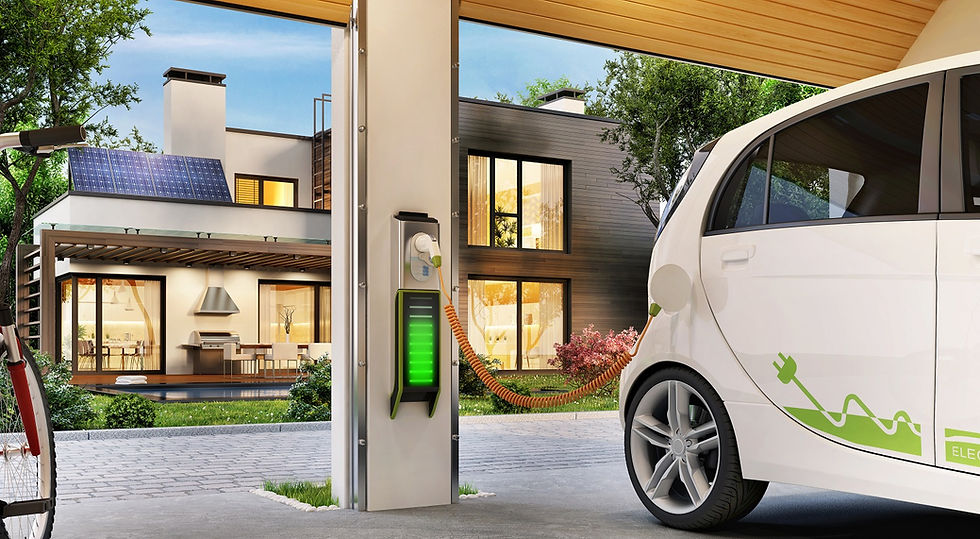

Image credit: renovationfind.com Fig.1 home charging infrastructure
We’ve truly entered the EV age and even though most of us will still go for the conventional Petrol or Diesel car if we were to buy a new car today, we know in the back of our minds that soon we would opt for the EV instead in the foreseeable future. Most believe that by 2025 Electric cars will almost totally replace conventional internal combustion engine cars as the first buying choice.
I wrote about where we stand on the EV motor technology last week in the last newsletter of 10th June 2022. If you would like to refer to this, it is here.
Moving on, let’s dive into the EV chargers today.
Chargers have today become the crucial factor in the success of EV technology. Even if you are a potential EV buyer, you would first like to consider the availability of EV chargers around the area in which you live or intend to travel. You do not want to be stranded in the middle of nowhere without your EV battery having a charge. You also want that if you need re-charge the time taken should be minimal.
Realizing the importance of the charging infrastructure, the Biden Administration is pursuing a goal of building and installing 500,000 DC charging stations across the country. While there are 160,000 gasoline stations for the IC engine cars across USA, there are only 4,000 charging stations; and 90% of these are from Tesla and that explains why Tesla is the number one choice in EVs today and way ahead of its competition. Tesla is creating an infrastructure of Solar powered charging stations on all highways and a Tesla EV can re-charged free on these. While all other EV makers are focusing and investing on the EVs, Tesla is deeply focusing and investing on the charging infrastructure. Remember that these charging stations need connectivity too for monitoring, control, and optimization. Also remember that the Tesla charger can be used only with Tesla EVs. You can see in Fig. 2 below that the Tesla connector is different.
All EVs except Tesla use the same J1772 connector for Level 2 charging. Tesla makes adapters that allow their vehicles to charge using J1772 and CHAdeMO connectors. Not all EVs have the option to use a DC fast charger, and sometimes it is available as an upgrade option. Be sure to research your model.

Image credit: duke-enery.com
The other thing we need to remember is that every EV comes with an On-Board Charger. This on-board charger is an electronic module which converts the input AC or DC to the right voltage and current required for battery charging inside the car. This is done by a “chopping” process. The on-board charger also ensures that the battery is initially charged with a constant current, thus maintaining speed and efficiency, and when the voltage of the battery reaches a certain value, it changes to constant voltage charging. This system is called the charging strategy and it is the most important function of the on-board charger.

Image courtesy: evexpert.eu
Now, let us look at the different types of chargers and their charging capability.

Image credit: duke-enery.com
Level 1 AC charger: Standard Wall Outlet (120 Volt AC)
Up to 5 miles of range per hour
No installation required – every EV will come with a standard Level 1 charger that you can drive home and plug into the wall.
Best used for overnight charging and low-mileage daily driving – a good option for plug-in hybrid vehicles because of their smaller batteries.
J1772 connector or Tesla connector (comes with vehicle)

Image credit: duke-enery.com
Level 2 AC charger: 240-Volt AC Outlet (Dryer Plug)
Average of 25 miles of range per hour
Often found in public areas (rest areas, shopping centers, restaurants, etc.)
Option to purchase and have it installed by a qualified electrician – can be either hardwired or plugged into an existing 240-volt outlet (dryer plug)
Best for quick charging – can get a full charge from empty overnight (8-10 hours)
J1772 connector or Tesla connector (comes with vehicle)

Image credit: duke-enery.com
DC Fast Charger
Fastest electric car charging option – provides up to 250 miles of range per hour, depending on the car and charging equipment
Can charge up to 80% typically in about 20 to 30 minutes. Charges at 200~600V, 100+ Amps, 50KW. However, new generations of DC fast chargers are gaining traction and can produce 150-350 kW of power.
Used to facilitate longer distance driving or road trips or for a quick recharge.
Most non-Tesla chargers have a CCS/SAE Combo connector. Tesla DC fast chargers will only work with Tesla vehicles.
Note that fast chargers may need cooling pipes to cool the contacts and keep them within 90 degrees C (see Fig. 3 below). High temperature develops on account of the high charging current which can reach up to 500A maximum. The balance 3 holes seen in the connector are for ground, control, and proximity detection.

Image credit: libertyplugins.com
The electric car typical layout for key components is given below for your ready reference.
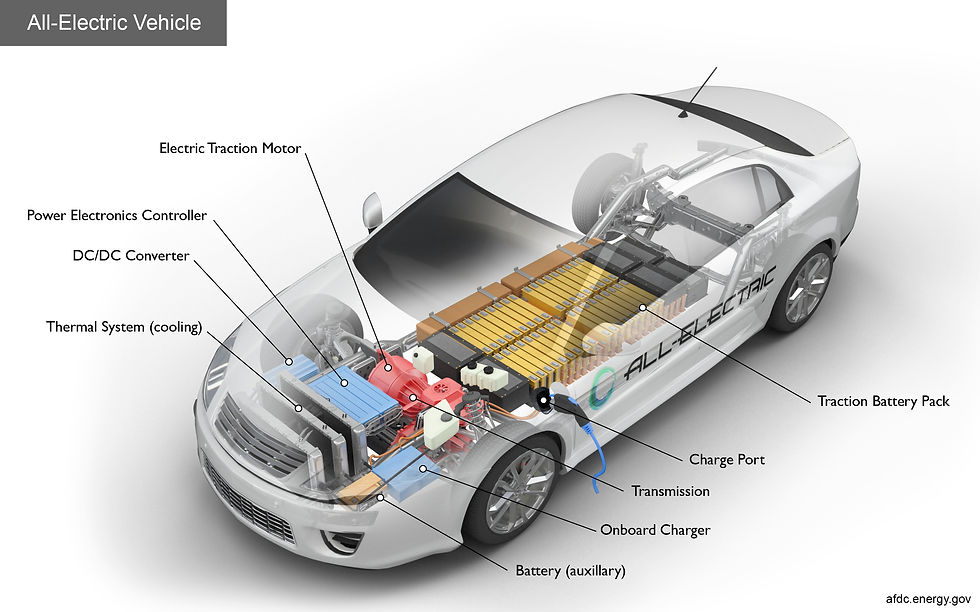
That’s all in this newsletter; more next week.
Please do subscribe to take full advantage of this newsletter.
Arun Bhatia
SUBSCRIBE: Join my subscription list with 1500+ people for tech updates and get a free copy of my eBook Tech Life- Picks>> Click here.

Get my eBook at a discounted price of Rs. 69 only here. https://amzn.to/3wUwmD4





Comments